Blog
Configuring Azure Backup Retention Policies

By Christodoulos Antoniadis – Engineer – Support Services
In the world of Microsoft Azure, where data is the heartbeat of every organization, securing it is an absolute must. This is where Microsoft Azure, the cloud computing service provided by Microsoft, comes into play. One of the key aspects of data protection in Azure is configuring backup retention policies. In this article, we will explore the options available for Azure Backup, what you can back up, and provide a comprehensive guide on how to configure retention policies effectively.
Understanding Azure Backup
Azure Backup is a flexible service that allows you to protect a wide range of data, including virtual machines, databases, files, and more. In IBSCY as Microsoft Gold partners in Cyprus, we recognize the vital significance of securing your data, and Azure Backup is a powerful tool at your disposal.
What Can You Backup with Azure Backup
Here are some of the Azure backup options available:
- Azure Virtual Machines (VMs): With Azure Backup, you can protect your VMs running in the Azure cloud. This ensures that your virtual infrastructure is safe and recoverable in case of disasters or data loss.
- On-Premises Servers: Azure Backup extends its support beyond the cloud by allowing you to back up your on-premises servers. This is particularly useful for organizations with a hybrid infrastructure.
- Microsoft Applications: Azure Backup integrates with popular Microsoft applications such as SQL Server, Exchange, SharePoint, and more. This means you can protect your critical business data within these applications.
- Azure File Shares: Organizations often store important data in Azure File Shares. Azure Backup can be used to back up these file shares to safeguard your valuable files and documents.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): For containerized applications running on AKS, Azure Backup offers protection, ensuring that your container data is recoverable when needed.
How to create Backup and edit Retention Policies
Now that we've explored the various options, let's dive into configuring retention policies for your Azure Backup. Here's a step-by-step guide to configure Azure VM backup and retention policy:
Step 1: Sign in to Azure portal and navigate to Virtual Machine
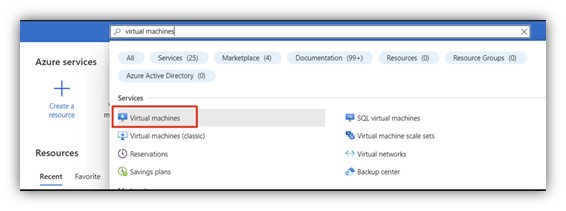 |
Step 2: Choose the VM to configure the back and from the side menu choose backup.
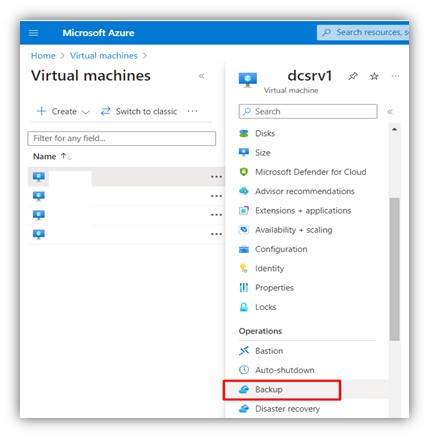 |
Step 3: Choose “edit this policy” to modify retention policy.
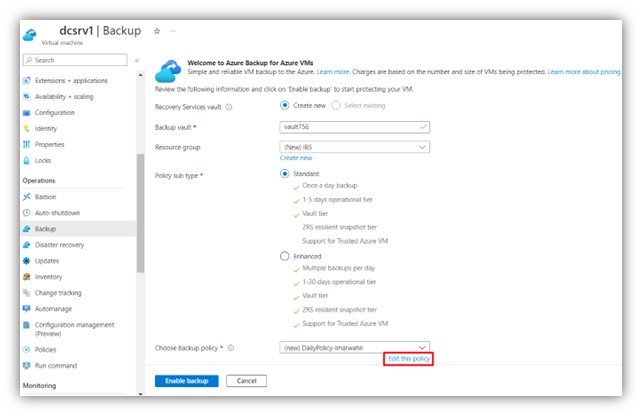 |
Step 4: Edit the policy as desired (as default the retention policy holds backup data for 30 days).
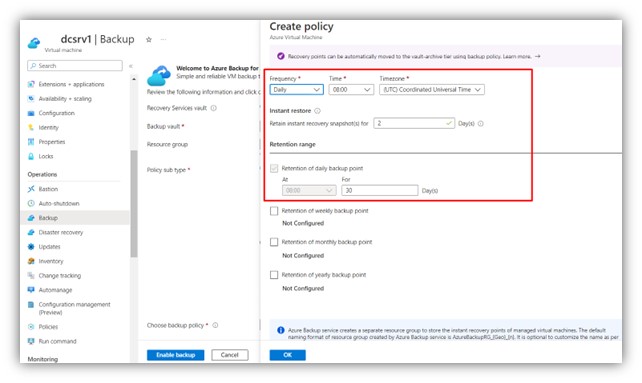 |
Step 5: Review and enable backup.
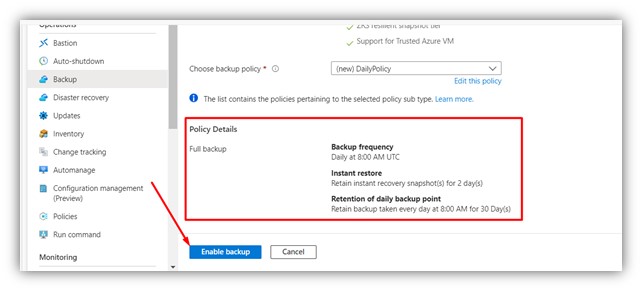 |
Conclusion
Configuring Azure Backup retention policies is a critical step in safeguarding your organization's data. With Azure Backup's flexibility and integration capabilities, you can protect a wide range of resources, from virtual machines to critical Microsoft applications. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you can ensure that your data remains secure and recoverable in the dynamic world of cloud computing. As Microsoft Gold partners in Cyprus, we are committed to helping you make the most of Azure services in Cyprus, ensuring the resilience and continuity of your business operations.
Reference list:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/backup/backup-during-vm-creation
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/backup/backup-overview
 |
Christodoulos Antoniadis joined the IBSCY team in 2021 at the technical department as a Systems Consultant and now, he is the Engineer in the Support Services. Among several qualifications, Christodoulos holds a BSc in Computer Science from University of Sunderland. |
