Blog
Configuring Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Using Microsoft Best Practices

Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) is an advanced, enterprise-grade security platform designed to provide comprehensive threat protection for your organization. Properly configuring MDE ensures that your endpoints are well-secured and capable of effectively detecting and responding to threats. This article will guide you through the best practices for configuring Microsoft Defender for Endpoint based on Microsoft's expert recommendations.
1. Pre-Configuration Steps
Before starting the configuration process, it is crucial to prepare your environment and ensure all necessary prerequisites are in place.
a. Ensure Licensing Requirement
Confirm that your organization has the appropriate licensing for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. The required licenses typically include Microsoft 365 E5, Microsoft 365 E5 Security, or a standalone Microsoft Defender for Endpoint license.
b. Verify System Requirements
Ensure that your devices comply with the system requirement for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. These requirements include specific operating system versions, hardware specification, and network configurations.
c. Set Up Appropriate Roles and Permissions
Assign the necessary roles and permissions to the IT staff respondible for managing Microsoft Defender for Endpoint within your Microsoft 365 tenant. Utilize Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) roles such as Security Administrator or Global Administrator to control access.
2. Onboarding Devices
Onboarding your devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is a fundamental initial step. This entails the installation of the required agent and the configuration of devices to ensure seamless communication with the MDE service.
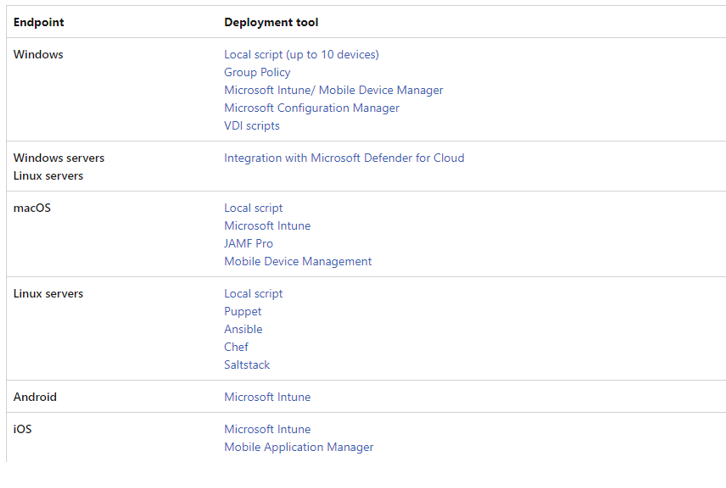
a. Choose Your Deployment Method
Microsoft offers several deployment methods, including:
- Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune)
- Group Policy
- Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager
- Script-based onboarding
Select the method that aligns with your organization's infrastructure and management capabilities.
b. Configure Device Onboarding
For example, to onboard devices using Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune):
- Create Device Configuration Profile: Navigate to Devices> Configuration profiles in the Intune portal, then create a new profile for Windows 10 and later.
- Select Endpoint Protection: Choose the Endpoint protection template.
- Configure Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: Under the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint section, configure the settings to enable the service and provide the onboarding package.
- Assign the Profile: Assign the profile to the device groups that you want onboard.
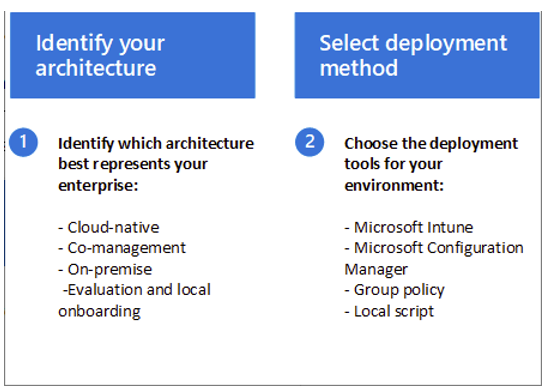
If you are already completed the steps to set up your Microsoft Defender for Endpoint deployment, and you have assigned roles and permissions for Defender for Endpoint, your next step is to create plan for onboarding. Your plan begins with identifying your architecture and choosing your deployment method.
c. Validate Onboarding
After onboarding, verify that the devices are correctly reporting to the MDE service. Check the Microsoft 365 Defender portal for a list of onboarded devices and their status.
3. Configuring Security Settings
Properly configuring security settings is crucial to ensure comprehensive protection. Microsoft recommends several key configurations.
a. Enable Real-Time Protection
Real-time protection is essential for detecting and stopping threats as they occur. Ensure that this setting is enabled across all devices. In Intune, this can be configured under the Endpoint protection profile.
b. Configure Cloud-Delivered Protection
Cloud-delivered protection leverages Microsoft's vast threat intelligence network to provide rapid detection and response capabilities. Ensure this setting is enabled to take advantage of real-time threat detection and blocking.
c. Turn On Tamper Protection
Tamper protection prevents unauthorized changes to security settings. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your security configuration. Enable tamper protection through Intune or via Group Policy.
d. Set Up Attack Surface Reduction (ASR) Rules
ASR rules help mitigate the risk of common attack vectors. Configure these rules based on your organization's risk profile and operational requirements. In Intune, these settings can be found under Endpoint security > Attack surface reduction.
4. Configuring Advanced Features
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint offers advanced features that enhance security capabilities.
a. Enable Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR provides detailed visibility into endpoint activities and advanced threat-hunting capabilities. Ensure EDR is enabled and configure appropriate alerting and response actions.
b. Use Automated Investigation and Response (AIR)
AIR capabilities help automate his investigation and remedation of threats, reducing the burden on security teams. Configure AIR settings to automatically respond to specific threats and scenarios.
c. Integrate with Microsoft Defender for Identity
Integrate MDE with Microsoft Defender for Identity to enhance identity-based threat detection. This integration provides additional context for threat investigations and response actions.
5. Monitor and Management
Ongoing monitoring and management are crucial for maintaining security.
a. Utilize the Microsoft 365 Defender Portal
The Microsoft 365 Defender portal is your central hub for managing and monitoring Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Regularly review security alerts, device health, and compliance status.
b. Configure Alert Notifications
Set up alert notifications to ensure timely response to security incidents. Configure email notifications and integrate with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems for centralized monitoring.
c. Regularly Review Security Recommendations
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint provides security recommendations based on observed threats and vulnerabilities. Regularly review and implement these recommendations to improve your security posture.
d. Conduct Threat Hunting
Utilize the threat-hunting capabilities within Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to proactively search for indicators of compromise. Leverage the advanced hunting queries in the Microsoft 365 Defender portal.
6. Training and Awareness
Ensuring that your IT and security teams are well-trained and aware of the latest features and best practices is essential.
a. Provide Training for Security Teams
Invest in training for your security teams on how to effectively use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft offrs a variety of training resources, including documentation, webinars, and certification programs.
b. Promote User Awareness
Educate end-users on best practices for maintaining security. This includes recognizing phishing attempts, reporting suspicious activities, and understanding the importance of updates and patches.
Conclusion
Implementing Microsoft Defender for Endpoint according to Microsoft's best practices requires a thorough and strategic approach. This involved proper onboarding, meticulous configuration of security settings, activation of advanced features, and continuous monitoring and management. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that your organization is robustly protected against sophisticated threats and upholds a strong security posture. Moreover, regular training and awareness initiatives significantly enhance the effectiveness of your endpoint security strategy by ensuring that both IT staff and end-users are well-prepared to tackle security challenges efficiently.
